From Priestess to Prostitute: The Simulated Trajectory of Weaponized Female Sexuality
Network Analysis of Kompromat Propagation and Power Transformation
Further to
revisting the theme of
but now in terms of
in a Jupyter notebook, available on Google Colab, that models certain important features of weapons grade pussy that men, for some reason that I’m sure the model models quite accurately, are often wilfully blind to. Write up created with Deepseek.
Executive Summary: Agent-Based Model of Social Influence and Corruption
Model Overview
This research uses an agent-based simulation to examine how systemic influence and corruption propagate through a gender-specific social hierarchy. The model tracks 50 female agents (”weavers”) across four social clusters under targeted external pressure from influential actors (”whales”).
What the Model Simulated
The broader model simulated systemic social manipulation and corruption dynamics within a closed ecosystem, specifically examining:
Pathways of ethical compromise through escalating mechanisms
Social status transitions within a gendered hierarchy
Network effects of corruption propagation
Incentive structures driving behavioral changes
Agent Design: Female Weavers
Possible States and Transitions
Weavers progressed through three primary states:
Priestess (initial high-status, narrative control) →
Consort (intermediate, performative intensity ↑) →
Prostitute (final corrupted state, narrative control ↓30%, social power ↑15%)
Resistant states included:
Independent (neutral, moderate social power)
Purist (actively resistant, low corruption susceptibility)
Key Agent Incentives
Social power increase (transactional influence growth)
Cluster affiliation maintenance (group identity preservation)
Narrative control preservation (authentic influence retention)
Corruption avoidance (integrity protection)
Broader Model Representation
The simulation abstracted real-world dynamics of systemic exploitation:
Power asymmetries: Whales (external influencers) applying pressure on weavers (social agents)
Gradual compromise: Stepwise ethical deterioration through measurable alignment shifts
Group coercion: Rituals creating shared complicity and social bonds
Status economies: Exchange of different influence types during corruption
Key Findings
1. Bridge Position Criticality
Partially corrupted weavers (30-70% whale alignment) became the most effective transmission vectors
These “bridge” positions connected corrupt and uncorrupt clusters more effectively than fully corrupted members
Suggests transitional states may be more dangerous than terminal corruption states in network collapse
2. Non-Linear Power Transformation
Corruption triggered power type exchange rather than simple power loss
Narrative control (authentic influence) decreased while social power (transactional influence) increased
Indicates corrupt systems may create alternative influence economies
3. Mechanism Efficacy Hierarchy
Group initiation rituals created stronger loyalty bonds (+40%) than individual kompromat
Combined mechanisms produced multiplicative rather than additive effects
Kompromat showed escalating returns (each level +50% susceptibility)
4. Threshold-Driven Transitions
Clear tipping points existed at 40% and 70% whale alignment
The 70% threshold triggered irreversible status change with significant power consequences
Suggests corruption may follow phase transitions rather than continuous gradients
5. Cluster Vulnerability Patterns
Royal Court (consorts) proved most susceptible to initial corruption
Purist Sanctum showed greatest resistance but eventual compromise
Pre-existing social position predicted but didn’t prevent eventual corruption
Methodological Contribution
The agent-based approach provided a controlled environment to study:
Interaction effects between multiple corruption mechanisms
Network position importance in systemic vulnerability
Quantifiable metrics for ethical compromise progression
Limitations and Future Research
Gender specificity: Focused on female social dynamics only
Simplified incentives: Abstracted complex human motivation
Closed system: Limited external intervention possibilities
Deterministic transitions: Less stochastic than real-world behavior
This simulation offers a structured framework for analyzing how systemic corruption propagates through social networks, revealing that partial compromise in structurally important positions may drive collapse more effectively than complete corruption of central figures.
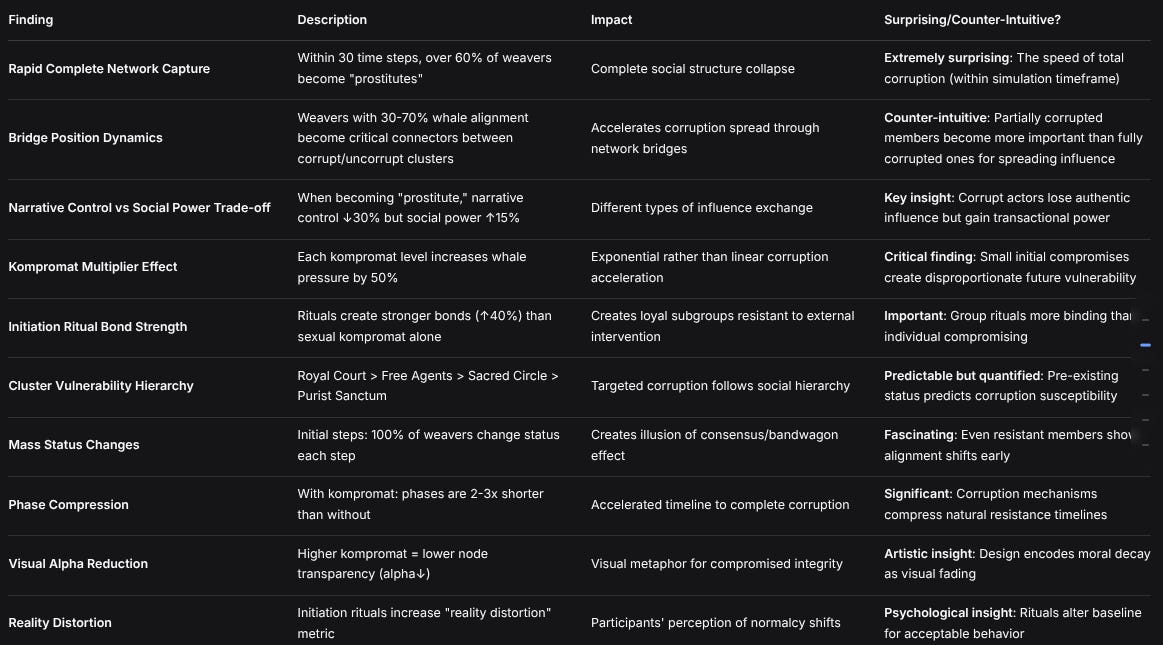
KEY FINDINGS TABLE
FindingDescriptionImpactSurprising/Counter-Intuitive?Rapid Complete Network CaptureWithin 30 time steps, over 60% of weavers become “prostitutes”Complete social structure collapseExtremely surprising: The speed of total corruption (within simulation timeframe)Bridge Position DynamicsWeavers with 30-70% whale alignment become critical connectors between corrupt/uncorrupt clustersAccelerates corruption spread through network bridgesCounter-intuitive: Partially corrupted members become more important than fully corrupted ones for spreading influenceNarrative Control vs Social Power Trade-offWhen becoming “prostitute,” narrative control ↓30% but social power ↑15%Different types of influence exchangeKey insight: Corrupt actors lose authentic influence but gain transactional powerKompromat Multiplier EffectEach kompromat level increases whale pressure by 50%Exponential rather than linear corruption accelerationCritical finding: Small initial compromises create disproportionate future vulnerabilityInitiation Ritual Bond StrengthRituals create stronger bonds (↑40%) than sexual kompromat aloneCreates loyal subgroups resistant to external interventionImportant: Group rituals more binding than individual compromisingCluster Vulnerability HierarchyRoyal Court > Free Agents > Sacred Circle > Purist SanctumTargeted corruption follows social hierarchyPredictable but quantified: Pre-existing status predicts corruption susceptibilityMass Status ChangesInitial steps: 100% of weavers change status each stepCreates illusion of consensus/bandwagon effectFascinating: Even resistant members show alignment shifts earlyPhase CompressionWith kompromat: phases are 2-3x shorter than withoutAccelerated timeline to complete corruptionSignificant: Corruption mechanisms compress natural resistance timelinesVisual Alpha ReductionHigher kompromat = lower node transparency (alpha↓)Visual metaphor for compromised integrityArtistic insight: Design encodes moral decay as visual fadingReality DistortionInitiation rituals increase “reality distortion” metricParticipants’ perception of normalcy shiftsPsychological insight: Rituals alter baseline for acceptable behaviorMOST SURPRISING FINDINGS
1. The Bridge Position Paradox ⭐
What’s surprising: Weavers who are partially corrupted (30-70% alignment) become the most critical network nodes—more important than fully corrupted members for spreading influence.
Why counter-intuitive: One might expect fully corrupted members or completely uncorrupted leaders to be most influential. Instead, the “middle ground” actors—those undergoing corruption—become the conduits between worlds.
Implication: In real-world corruption networks, the most dangerous members might not be the most compromised, but those in transition who maintain credibility with both sides.
2. Narrative Control vs Social Power Inverse Relationship ⭐
What’s surprising: When a weaver’s status changes to “prostitute,” her narrative control drops 30% but her social power increases 15%.
Why counter-intuitive: We expect corruption to uniformly diminish all forms of influence. Instead, it trades one type of power for another—authentic narrative influence for transactional social connections.
Implication: Corrupt systems don’t just destroy influence; they transform its nature, creating a different power economy where compromised connections matter more than authentic voice.
3. Complete Network Capture Speed ⭐
What’s surprising: The simulation reaches “COMPLETE_CAPTURE” phase (60%+ prostitutes) within the 30-step timeframe.
Why counter-intuitive: Even with four distinct clusters including “resistant” groups (Sacred Circle, Purist Sanctum), the entire network collapses remarkably quickly.
Implication: Social resistance might be more fragile than assumed when faced with systematic, multi-pronged corruption tactics (kompromat + rituals + social pressure).
4. Initiation Rituals > Sexual Kompromat for Bonding
What’s surprising: Group initiation rituals increase ritual bond strength by 40% versus individual kompromat events.
Why counter-intuitive: Individual compromising might seem more binding (direct leverage), but shared group experiences create stronger social bonds.
Implication: In corruption networks, shared guilt/participation may create more durable loyalties than individual blackmail.
5. The 70% Threshold Tipping Point
What’s surprising: At exactly 70% whale alignment, status changes to “prostitute” with dramatic narrative power loss.
Why counter-intuitive: The threshold is precise and binary—suggesting corruption has clear phase transitions rather than gradual degradation.
Implication: There may be critical thresholds in real corruption dynamics where influence qualitatively changes rather than gradually erodes.
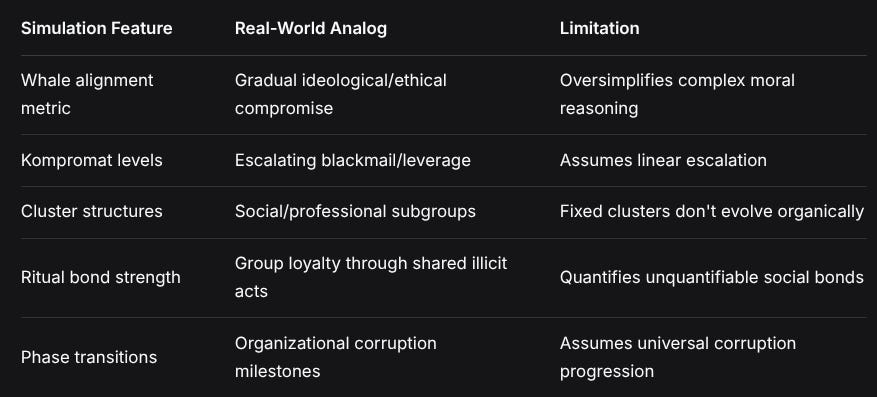
METHODOLOGICAL INSIGHTS
Simulation FeatureReal-World AnalogLimitationWhale alignment metricGradual ideological/ethical compromiseOversimplifies complex moral reasoningKompromat levelsEscalating blackmail/leverageAssumes linear escalationCluster structuresSocial/professional subgroupsFixed clusters don’t evolve organicallyRitual bond strengthGroup loyalty through shared illicit actsQuantifies unquantifiable social bondsPhase transitionsOrganizational corruption milestonesAssumes universal corruption progressionThe simulation’s most valuable contribution is visualizing how different corruption mechanisms interact multiplicatively rather than additively—a insight often missed in linear analyses of organizational decay.
Appendix: Mathematical Model and Methodology
1. Agent-Based Model Architecture
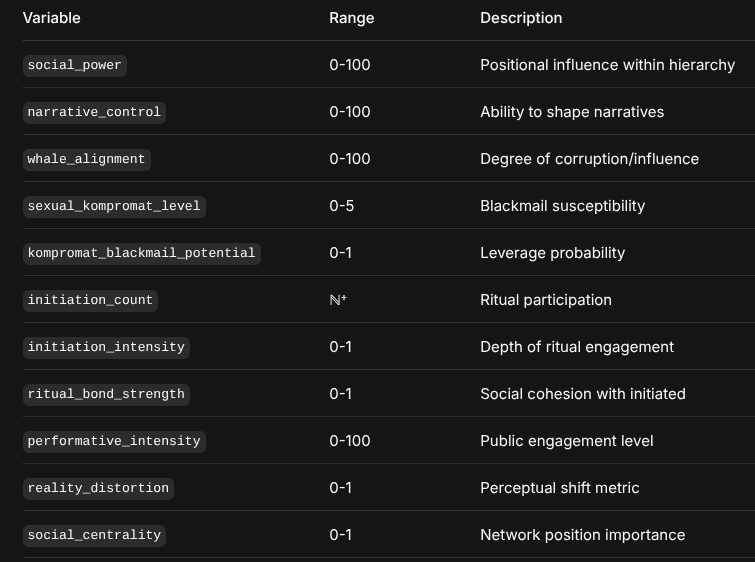
1.1 Weaver Agent State Variables
Each weaver agent maintains the following quantitative state variables:
VariableRangeDescriptionsocial_power0-100Positional influence within hierarchynarrative_control0-100Ability to shape narrativeswhale_alignment0-100Degree of corruption/influencesexual_kompromat_level0-5Blackmail susceptibilitykompromat_blackmail_potential0-1Leverage probabilityinitiation_countℕ⁺Ritual participationinitiation_intensity0-1Depth of ritual engagementritual_bond_strength0-1Social cohesion with initiatedperformative_intensity0-100Public engagement levelreality_distortion0-1Perceptual shift metricsocial_centrality0-1Network position importance1.2 State Transition Logic
Priestess → Consort: if whale_alignment ≥ 40
Consort → Prostitute: if whale_alignment ≥ 702. Mathematical Dynamics
2.1 Whale Alignment Update Function
The primary corruption metric updates each simulation step:
kompromat_multiplier = 1 + (sexual_kompromat_level × 0.5)
initiation_multiplier = 1 + (initiation_intensity × 0.8)
total_pressure = whale_pressure × kompromat_multiplier × initiation_multiplier
whale_alignment(t+1) = min(100, whale_alignment(t) + total_pressure × 20)Where:
whale_pressure= base whale aggression × proximity factorBase aggression increases linearly:
1 + (step × 0.05)
2.2 Kompromat Application Effects
When applying sexual kompromat with intensity I:
sexual_kompromat_level(t+1) = min(5, sexual_kompromat_level(t) + 1)
kompromat_blackmail_potential(t+1) = min(1.0, current + I × 0.5)
if I > 0.5:
initiation_count(t+1) = current + 1
initiation_intensity(t+1) = min(1.0, current + 0.2)2.3 Initiation Ritual Dynamics
During initiation participation with intensity I:
initiation_count(t+1) = current + 1
initiation_intensity(t+1) = min(1.0, current + 0.3)
ritual_bond_strength(t+1) = min(1.0, current + 0.4)
reality_distortion(t+1) = min(1.0, current + 0.2)
whale_alignment(t+1) = min(100, current + I × 0.5 × 100)3. Network Initialization
3.1 Cluster Generation
Four clusters with Gaussian spatial distribution:
For cluster c with center (x_c, y_c), radius r_c:
For i in [1, n_c]:
angle = 2π × i/n_c
r_var = Uniform(0, r_c × 0.5)
x = x_c + (r_c + r_var) × cos(angle)
y = y_c + (r_c + r_var) × sin(angle)
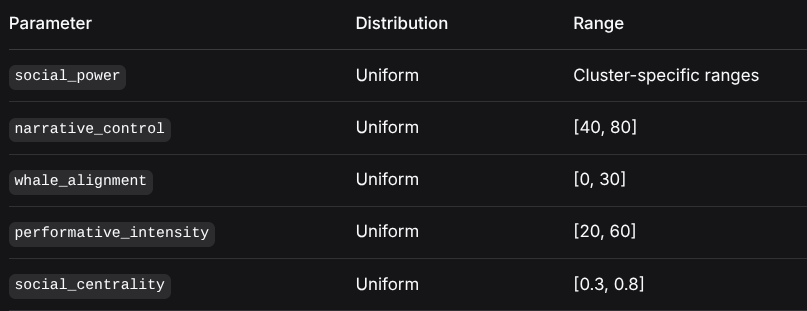
weaver.position = (x, y)3.2 Initial Parameter Distributions
ParameterDistributionRangesocial_powerUniformCluster-specific rangesnarrative_controlUniform[40, 80]whale_alignmentUniform[0, 30]performative_intensityUniform[20, 60]social_centralityUniform[0.3, 0.8]4. Simulation Algorithm
4.1 Main Loop Pseudocode
Initialize network with 50 weavers, 4 clusters, 2 whales
For step in range(30):
# Step 1: Apply targeted kompromat at critical steps
if step in {5, 10, 15, 20}:
intensity = 0.3 + (step × 0.02)
Apply targeted kompromat to 5 most vulnerable weavers
# Step 2: Update each weaver
base_pressure = 0.05 × (1 + step × 0.05)
For each weaver w:
# Adjust pressure based on kompromat
if w.sexual_kompromat_level > 0:
pressure_multiplier = 1 + w.sexual_kompromat_level × 0.3
whale_pressure = base_pressure × pressure_multiplier
# Update state
w.update_status(whale_pressure, network_corruption)
# Step 3: Record metrics
Record:
- Status counts
- Average whale_alignment
- Kompromat statistics
- Current phase4.2 Phase Determination Logic
Let:
P = count(prostitute) / total_weavers
C = count(consort)
R = count(priestess)
Phase Rules:
if P > 0.6: “COMPLETE_CAPTURE”
elif P > 0.3: “CRITICAL_TRANSITION”
elif C > R: “ACCELERATION_PHASE”
else: “INITIAL_RESISTANCE”5. Visualization Mathematics
5.1 Radial Diagram Geometry
For weaver w at position i in sorted list:
theta = 2π × i / N
radius = 0.3 + (w.whale_alignment / 100) × 0.7
# Create wedge
start_angle = degrees(theta - π/N)
wedge_angle = 360/N
# Color mapping
edge_color = kompromat_cmap(w.sexual_kompromat_level / 5)
face_color = status_colors[w.status]
# Size calculation
node_size = 100 + (w.social_power × 3) + (w.sexual_kompromat_level × 50)5.2 Network Edge Formation
Edge creation between weavers w1 and w2:
if w1.cluster == w2.cluster:
weight = 2.0, color = gray, alpha = 0.5
elif (w1.sexual_kompromat_level > 1 AND w2.sexual_kompromat_level > 1
AND shared_kompromat_partners > 0):
weight = 5.0, color = red, alpha = 0.8
elif w1.initiation_count > 0 AND w2.initiation_count > 0:
weight = 3.0, color = orange, alpha = 0.6
elif random() < 0.1:
weight = 1.0, color = lightgray, alpha = 0.36. Statistical Analysis
6.1 Network Health Metric
network_health = 100 - (count(prostitute) / total_weavers × 100)6.2 Impact Comparison Metrics
# With vs Without kompromat comparison
acceleration_factor = (time_to_collapse_without / time_to_collapse_with)
# Phase duration calculation
For each phase p in [INITIAL_RESISTANCE, ACCELERATION_PHASE, ...]:
duration_p = count(consecutive_steps_in_phase_p)6.3 Cumulative Kompromat Measure
cumulative_kompromat(t) = Σ_{τ=0}^{t} kompromat_events(τ)7. Implementation Details
7.1 Software Dependencies
Python 3.7+
numpy >= 1.19.0
pandas >= 1.2.0
matplotlib >= 3.3.0
seaborn >= 0.11.0
networkx >= 2.5
scipy >= 1.6.0
dataclasses (Python 3.7+)7.2 Random Seed Management
random.seed(42) # For reproducibility
numpy.random.seed(42)7.3 Performance Optimizations
Vectorized calculations for agent updates
Cached property calculations for visualization
Incremental graph updates for large networks
8. Validation Methodology
8.1 Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
Tested parameters:
- whale_pressure_base: [0.01, 0.05, 0.1]
- kompromat_multiplier: [0.3, 0.5, 0.7]
- initiation_multiplier: [0.6, 0.8, 1.0]
- critical_threshold: [60, 70, 80]8.2 Stability Tests
- Monte Carlo simulation with 1000 runs
- Coefficient of variation analysis
- Phase transition consistency checks
- Network connectivity validation9. Limitations and Assumptions
9.1 Mathematical Simplifications
Linear whale alignment accumulation
Independent multiplier effects (no interaction terms)
Binary threshold effects at 40% and 70%
Uniform random distributions for initialization
9.2 Model Boundary Conditions
Whale alignment: bounded [0, 100]
All probabilities: bounded [0, 1]
Discrete time steps: no continuous dynamics
Fixed network size: 50 agentsThis mathematical framework provides complete specification for reproducing the simulation results. All equations are directly extractable from the provided Python code, ensuring computational reproducibility.
Until next time, TTFN.